White Line Disease Symptoms
White line disease symptoms. The life expectancy after a. The farrier might also notice a hollow sound when he taps the outside of the hoof wall with a hammer. Initial stages of white line disease include white chalky powdery areas at the white line.
White line disease may be diagnosed during a routine trimming when a farrier notices a small area of crumbly or powdery black or gray tissue at the white line. White line disease has many other names. Often the farrier is the first to detect white line disease during a routine trimming or shoeing procedure.
White Line Disease is a widening of the white line. The most common culprit is fusobacterium necrophorum which causes a variety of diseases including navel illjoint ill in foals diphtheria in calves and foot rot. The fungus involved likes to digest away keratin which is what makes hair and fingernails but bacteria often are isolated with it too.
Swelling of the heel bulb represents the most advanced form of white line disease. Thrush affecting the sulci of the frog and sometime deeper tissues is generally caused by bacteria. This list goes on.
It is frequently misdiagnosed as footrot often presented as a case of footrot resistant to treatment. Occurs in approximately 70 to 80 percent of infected persons. It may also give off a foul odor.
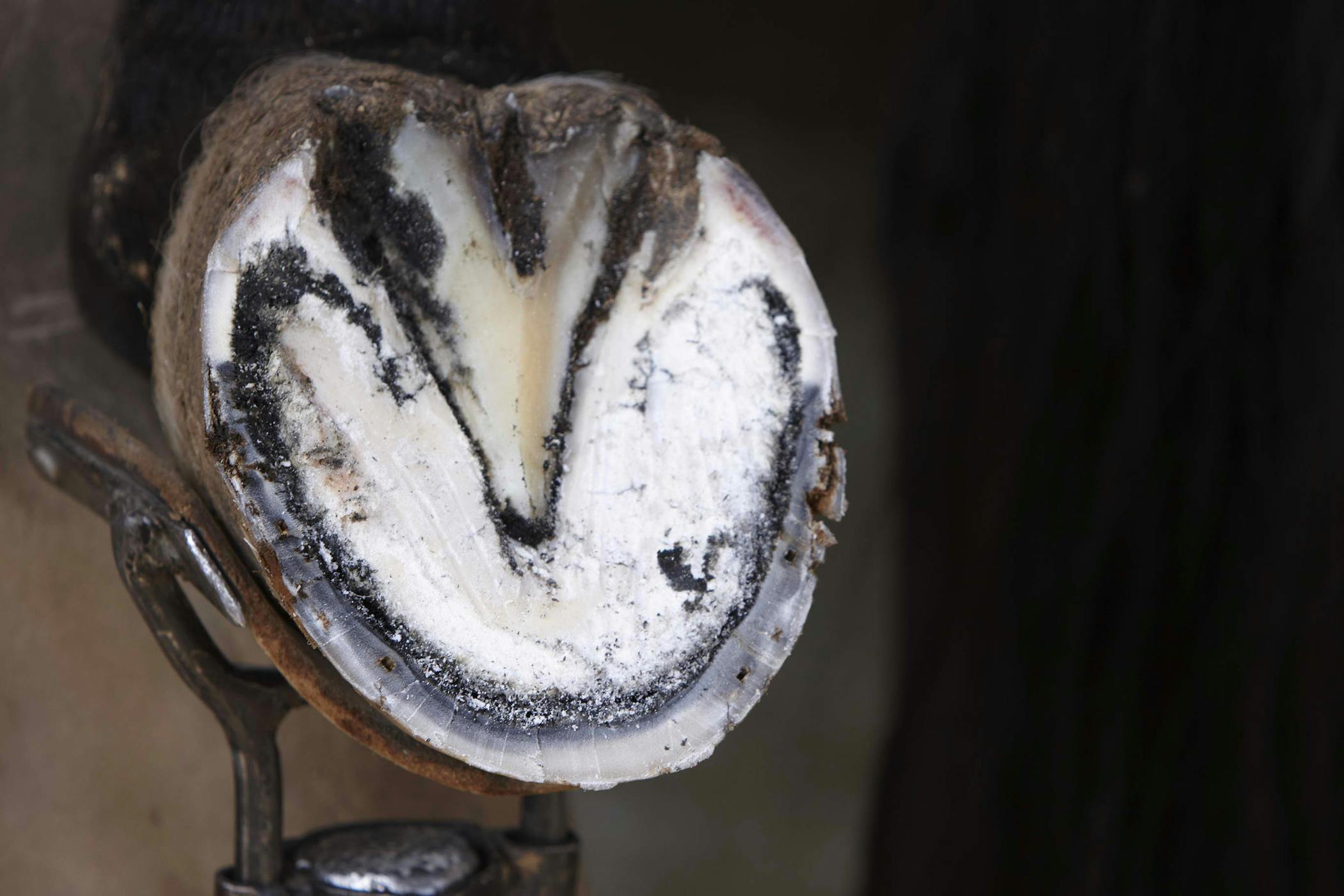
The white line is the connection between the inner hoof wall and the sole. Lameness is often not present unless the disease is advanced. Stall rot hollow foot wall thrush and seedy toe.
Ironically white line disease does not infect the white line. Footrot causes the whole foot to swell evenly to the fetlock.
Footrot causes the whole foot to swell evenly to the fetlock.
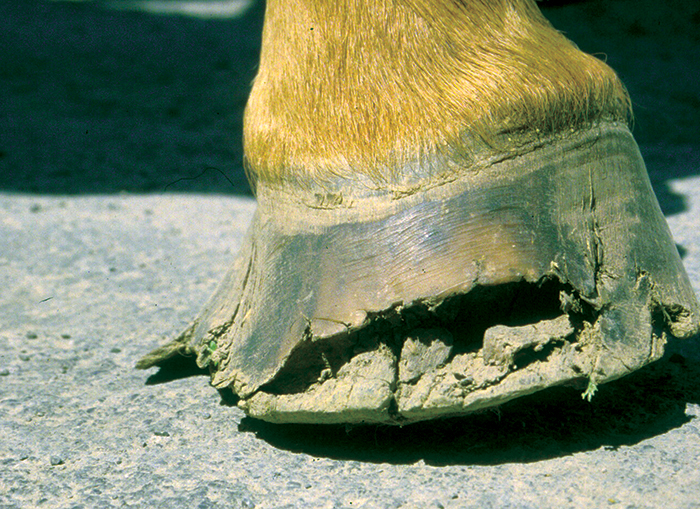
This list goes on. The telltale signs are stretched white lines and deep grooves filled with rotting material where healthy hoof walls and white lines should be flares that wont grow out hooves that wont hold a shoe persistent wall cracks soles that remain flat in spite of the most diligent care and recurring abscesses. Another early sign is a widening of the sole-wall junction. Erythema migrans EM rash see photos. For ease of our discussion in this article well refer to this problem as white line disease. Paring away the damaged horn reveals separation of the hoof layers leading upward from the toe toward the coronary band. Lameness is often not present unless the disease is advanced. Often the farrier is the first to detect white line disease during a routine trimming or shoeing procedure. Headaches dizziness fever Other common flu-like symptoms are headaches dizziness fever muscle pain and malaise.
White line disease has many other names. The farrier might also notice a hollow sound when he taps the outside of the hoof wall with a hammer. It is frequently misdiagnosed as footrot often presented as a case of footrot resistant to treatment. Erythema migrans EM rash see photos. The most common culprit is fusobacterium necrophorum which causes a variety of diseases including navel illjoint ill in foals diphtheria in calves and foot rot. The telltale signs are stretched white lines and deep grooves filled with rotting material where healthy hoof walls and white lines should be flares that wont grow out hooves that wont hold a shoe persistent wall cracks soles that remain flat in spite of the most diligent care and recurring abscesses. Paring away the damaged horn reveals separation of the hoof layers leading upward from the toe toward the coronary band.





































Posting Komentar untuk "White Line Disease Symptoms"