three stage of stress
 General Adaptation Syndrome: Your Body's Response to Stress
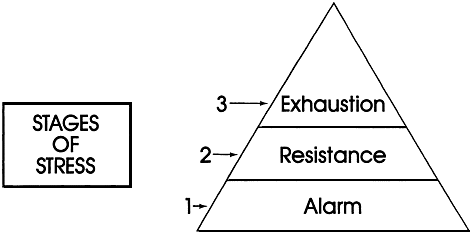
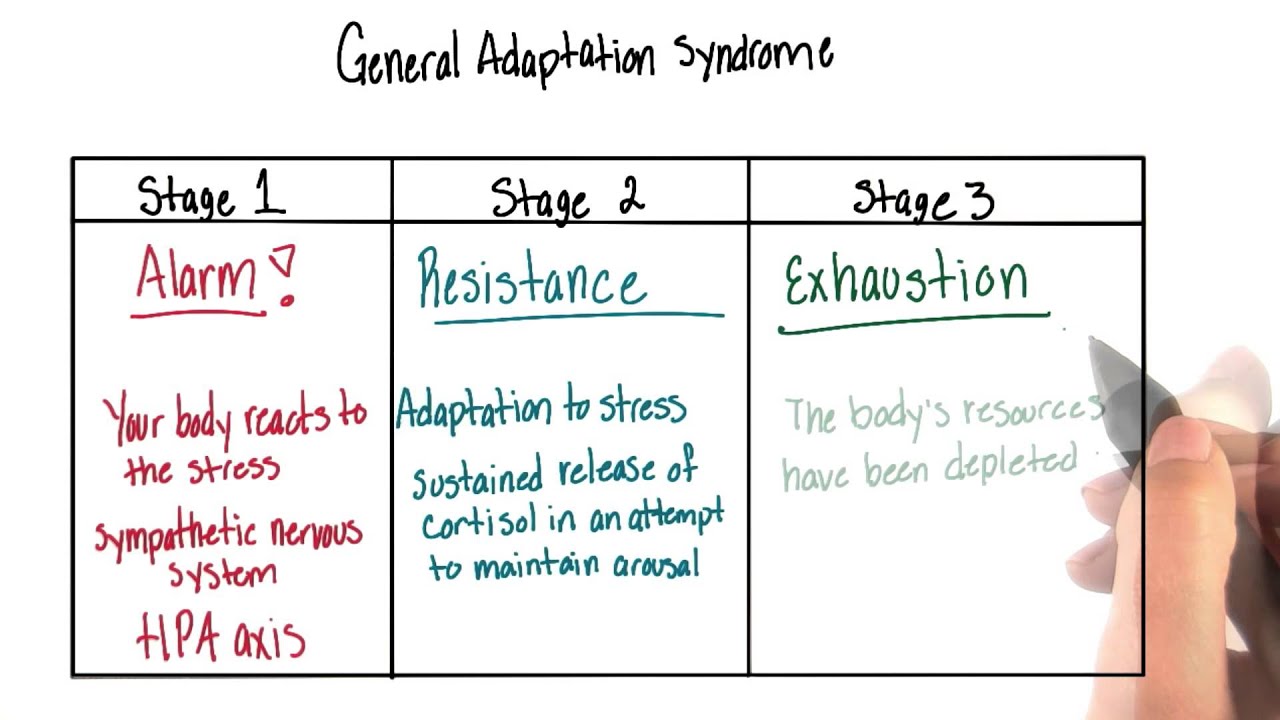
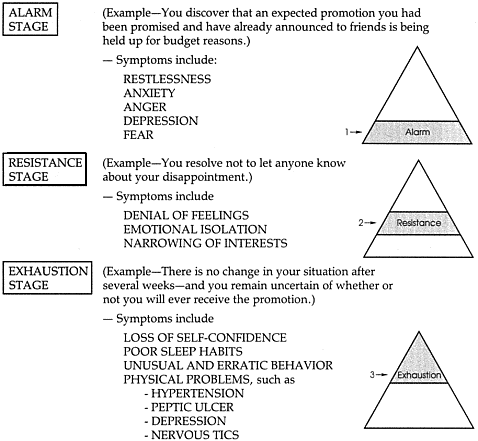
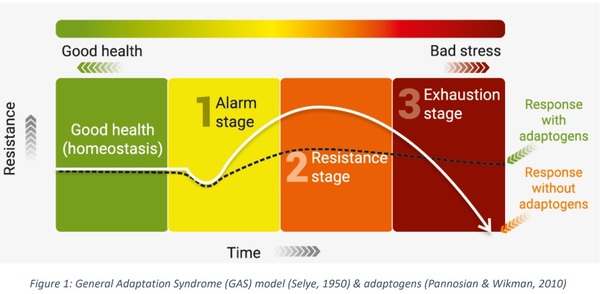
General Adaptation Syndrome: Your Body's Response to StressWhat to know about general adaptation syndromeGeneral adaptation syndrome is a three-stage response that the body has to emphasize. But what do the different stages imply and what examples are of GAS in action? Sometimes it is thought as a mental pressure, but it also has a physical effect on the body. Understanding the stages that the body passes when exposed to stress helps people to be more aware of these physical signs of stress when they occur. This article explores what general adaptation syndrome (GAS) is, its different stages, and when it can occur. It also considers how people can better manage their stress response. Quick data on the GAS:Hans Selye, a scientist born in Vienna, who worked in the 20th century, was the first person to describe the GAS. Selye found that rats showed a similar set of physical responses to several different stress factors. The latter included cold temperatures, excessive physical efforts and toxin injection. The scientist explained to the GAS as the body's way of adapting to a perceived threat to better equip it to survive. In 1946 a paper on Selye's GAS theory was published. The three stages of the GAS are: What happens within the body during each of these stages is explored below. Alarmed reaction stage In the alarm reaction stage, a relief signal is sent to a part of the brain called the hypothalamus. Hypothalamus allows the release of hormones called glucocorticoids. Glucocorticoids activate the release of adrenaline and cortisol, which is a stress hormone. Adrenaline gives a person a boost of energy. His heart rate increases and increases. Meanwhile, blood sugar levels also rise. These physiological changes are governed by a part of the autonomic nervous system of a person (ANS) called a sympathetic branch. The alarm reaction stage of the GAS prepares a person to respond to the stressors they are experiencing. This is often known as a "light or flight" response. ResistanceDuring the resistance stage, the body tries to counter the physiological changes that occurred during the alarm reaction phase. The resistance stage is governed by a part of the ANS called parasympathetic. The ANS parasympathetic branch tries to return the body to normal by reducing the amount of cortisol produced. Heart rate and blood pressure begin to return to normal. If the stressful situation comes to an end, during the resistance stage, the body will return to normal. However, if the stressor remains, the body will remain alert, and stress hormones continue to be produced. This physical response can lead a person struggling to concentrate and become irritable. Depletion Stage After a long period of stress, the body enters the final stage of the GAS, known as the stage of exhaustion. At this stage, the body has exhausted its energy resources by continually trying, but failing to recover from the initial stage of alarm reaction. Once it reaches the stage of exhaustion, a person's body is no longer equipped to fight stress. They may experience: If a person does not find ways to manage stress levels at this stage, he or she risks developing stress-related health conditions. Selye's study was limited to physical stress factors, such as cold temperatures and physical overexertion. However, it is now understood that the events of life that induce psychological stress cause the same physical reactions, as was observed in Selye's study. The kind of life events that can cause a person to experience stress and GAS include: In theory, the fact that these situations can cause GAS can be beneficial. The alarm reaction gives people an explosion of energy and concentration that could help them solve problems. For most people, however, the physical response that your body passes when under stress is not helpful. Unlike the threats that people may have faced in the Stone Age, a person today is unlikely to be able to solve a stressful situation of modern life with an explosion of energy. Long-term stress can have a negative impact on a physical person and on his or her immune system. A noted that chronic stress could: Another explains that chronic stress is also related to a higher risk. The first step to control GAS is to understand what triggers stress. Different things trigger stress for different people. It is important for a person to identify which situations and events are especially stressful for them. Then it can be possible to make lifestyle changes to reduce exposure to these triggers. For example, a long journey can be stressful. If so, moving rolework somewhere closer to home, or asking to work remotely, can help. When it is not possible to avoid a stress trigger, it is important to find a way to reduce the impact it has on the body and mind. The recommended physical activity as a way of reducing stress. Exercise releases endorphins, which improve sleep and promote a sense of well-being. Walking or risking are easy ways to exercise. The following activities can also help: Stress causes physical changes in the body. GAS is a three-stage process that the body passes when exposed to stressful events. Long-term stress has a negative impact on physical and mental well-being. The final physical stage of the GAS is known as exhaustion and can occur when a person is exposed to stress for long periods of time. This, in turn, makes them more vulnerable to stress-related diseases. Understanding stress triggers can help someone make lifestyle changes to reduce stress. When this is not possible, finding ways to manage the impact of stress on the body and mind is critical. Stress management may include activities such as deep breathing, yoga, mental care or meditation. Last medical review on 28 November 2017Most recent newsRelated coverage
According to the General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS), how many stages of stress are there? | Socratic

Hormones and Stress
General adaptation syndrome - Intro to Psychology - YouTube

Three stages of stress corrosion crack propagation | Download Scientific Diagram

Ch04 01

Example Of The Three Stages of Stress | Stress, University, Login page

The General adaptation syndrome (GAS) are the stages that some people go through when dealing with stress. These three st… | What is stress, Stress, Stress reaction
Explaining Stress: The General Adaptation Model

Unit 2 Mental & Emotional Health Managing Stress and Coping with Loss. - ppt download

It's Been a Hell of a Week – Give Yourself Healing Time – Life Horizons
Understanding Stress : Add Balance To Your Life, Stages Of Stress, Understanding The Three Basic Stages Of Stress
GAS, that weakens the general immunity in chickens - Engormix

3.2 Emotions, Stress, and Well-Being – Principles of Social Psychology

3 Stages of Stress | How body response in those Stages | MHA

Describe the Gas Model and Illustrate the Relevance of this Model with the Help of an Example. - Psychology | Shaalaa.com
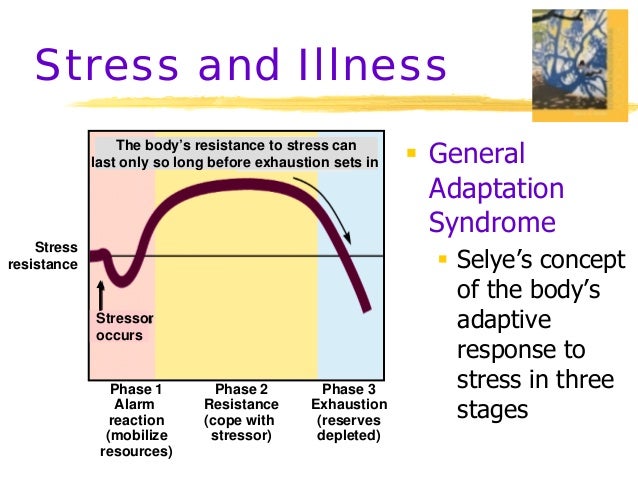
Stress Causes, Effects and Management. By Dr. Ali Garatli
Stress Management - What is stress?

Strain vs. Stress: A Small but Significant Distinction — The Aspen Triathlon Club

Three stages of stress corrosion crack propagation | Download Scientific Diagram

What Are The Three Stages Of Stress And How To Cope | BetterHelp

VCE Psychology Unit 3 -AOS 1 Stress as a Psychobiological Process Flashcards | Quizlet

Sutramdyti Supyk Huh general adaptation syndrome - yenanchen.com
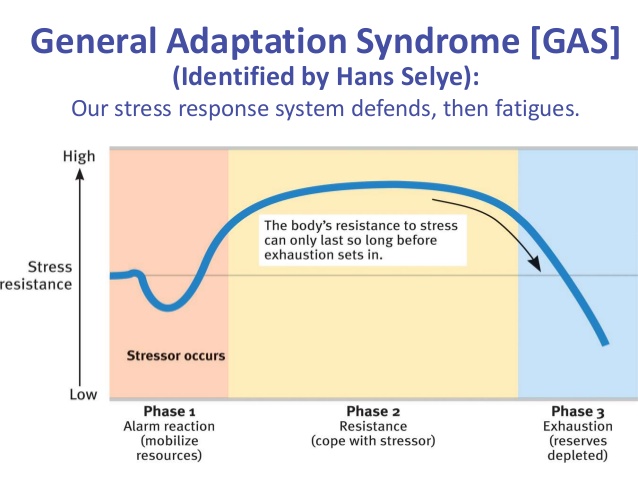
Eustress, I stress, We All Stress- And We Adapt To It — Musicians' Health Collective

Section 3.2 How Stress Affects Your Body Slide 1 of 11 Objectives List in order the three stages of the body's response to stress. Identify four types. - ppt download
An example of social wellness would be going to a pa...

The Latest Research on Resilience, Recovery, and HRV - Biostrap
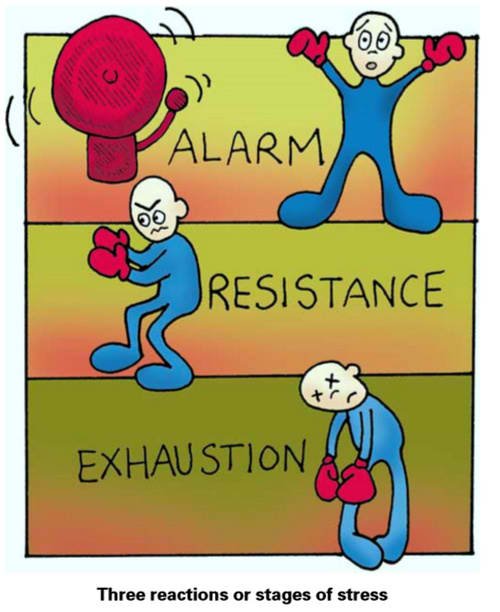
STRESS-series: People's Reactions to Stress — Steemit

The three stages of stress relaxation - Observations for the time-dependent behaviour of brittle rocks based on laboratory testing - ScienceDirect

Exhaustion Stage of Stress: Psychology Overview - Abnormal Psychology Class (Video) | Study.com

Brain Strength Academy (martywolner) - Profile | Pinterest

Chapter 14 Vocab Flashcards | Quizlet

a) Schematic illustration of a typical stress relaxation curve... | Download Scientific Diagram

General adaptation syndrome: What it is, stages, and examples

What Are The Three Stages Of Stress And How To Cope | BetterHelp

The 5 stages of stress every student needs to know

StReSs. What Is Stress? The body's response to a stressor. Stressor: an idea or thing that makes a person anxious. In order to stay alive, the human brain. - ppt download

The 5 stages of stress every student needs to know
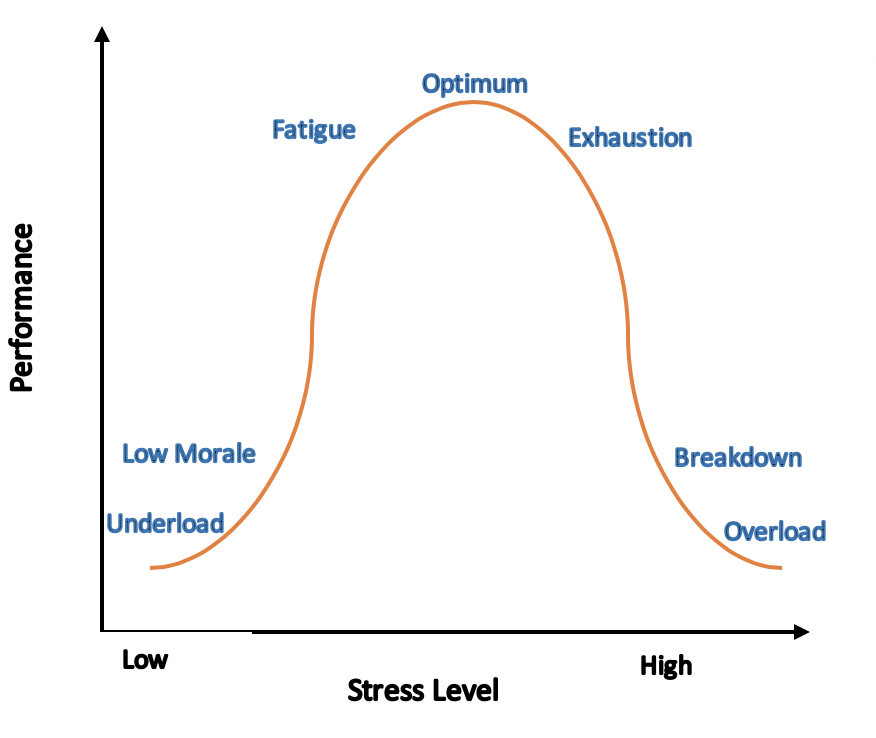
Allostatic load - Wikipedia

Changes in the body's response to stress and the reward system over the... | Download Scientific Diagram

The General Adaptation Syndrome by Hans Selye
Posting Komentar untuk "three stage of stress"